1. What's A Flooded Lead Acid Battery?
The flooded lead acid battery (FLA battery) is the most common lead acid battery type and has been in use over a wide variety of applications for over 150 years.
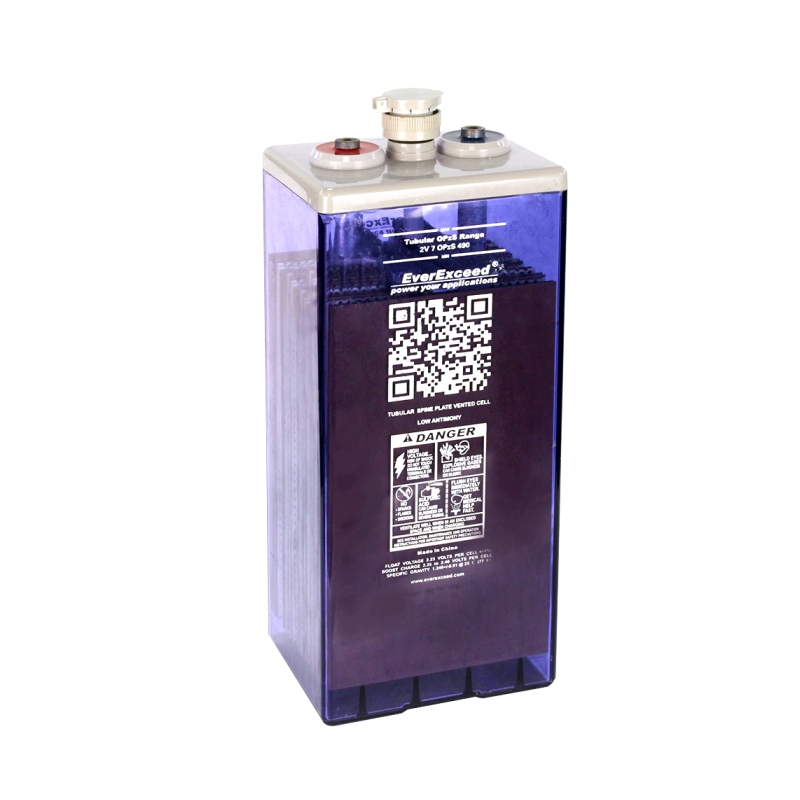
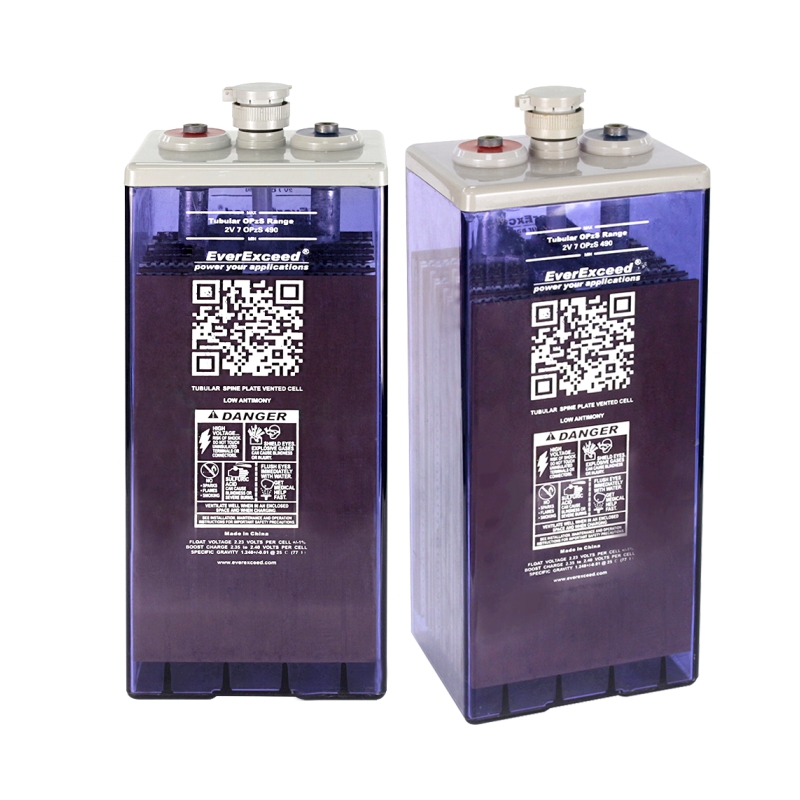
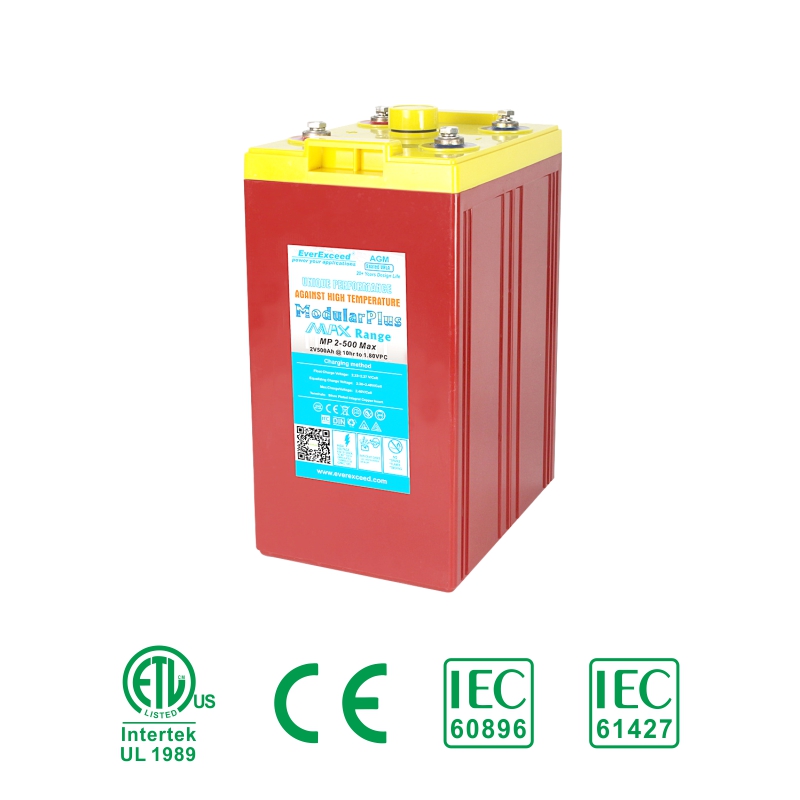
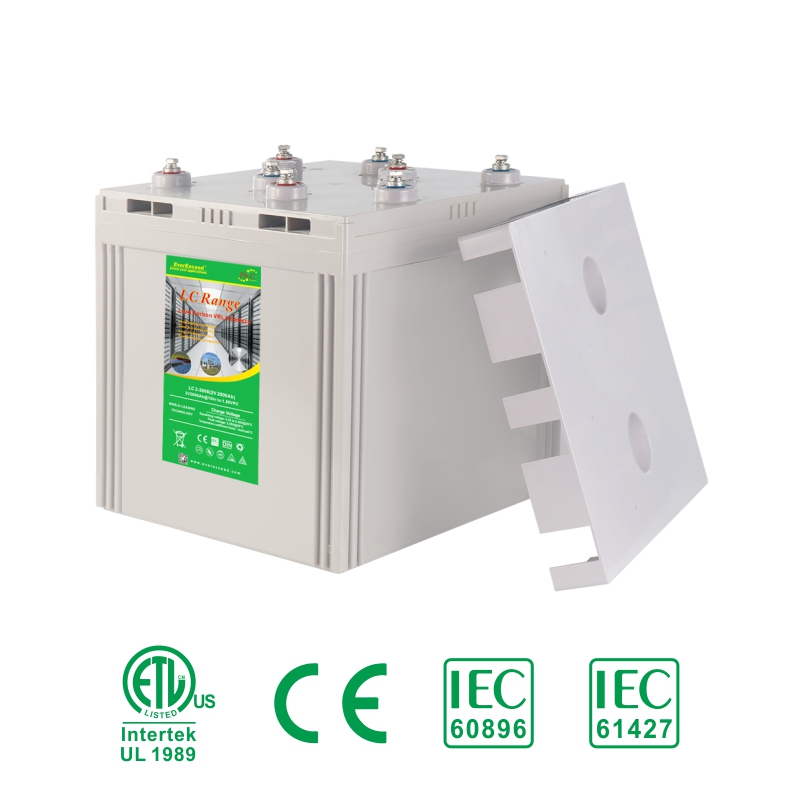
The sulfuric acid in the electrolyte of a lead acid battery is directly involved in the charging and discharging process of the battery. In a traditional lead acid battery, the remaining space in the battery tank after removing the electrode plates, partitions, and other solid assembly parts is completely filled with sulfuric acid electrolyte, and the electrolyte is in a state of surplus and excess, which is therefore known as the "flooded" type of battery, in which the electrode plates of the battery are completely immersed in the sulfuric acid electrolyte. electrolyte.
In contrast, if the remaining space in the battery tank is not completely filled with electrolyte, and the plates are not completely immersed in the electrolyte, it is called a "liquid-poor" battery.
Liquid-rich battery has a cover on the top that can ventilate and prevent liquid from spilling out (but not completely prevent liquid leakage), due to evaporation and decomposition loss of water in the process of use, it is necessary to open the cover periodically to refill distilled water and adjust the density of the electrolyte, so it is customarily referred to as the "open-type" batteries.
2.What are the main application characteristics of Flooded Battery?
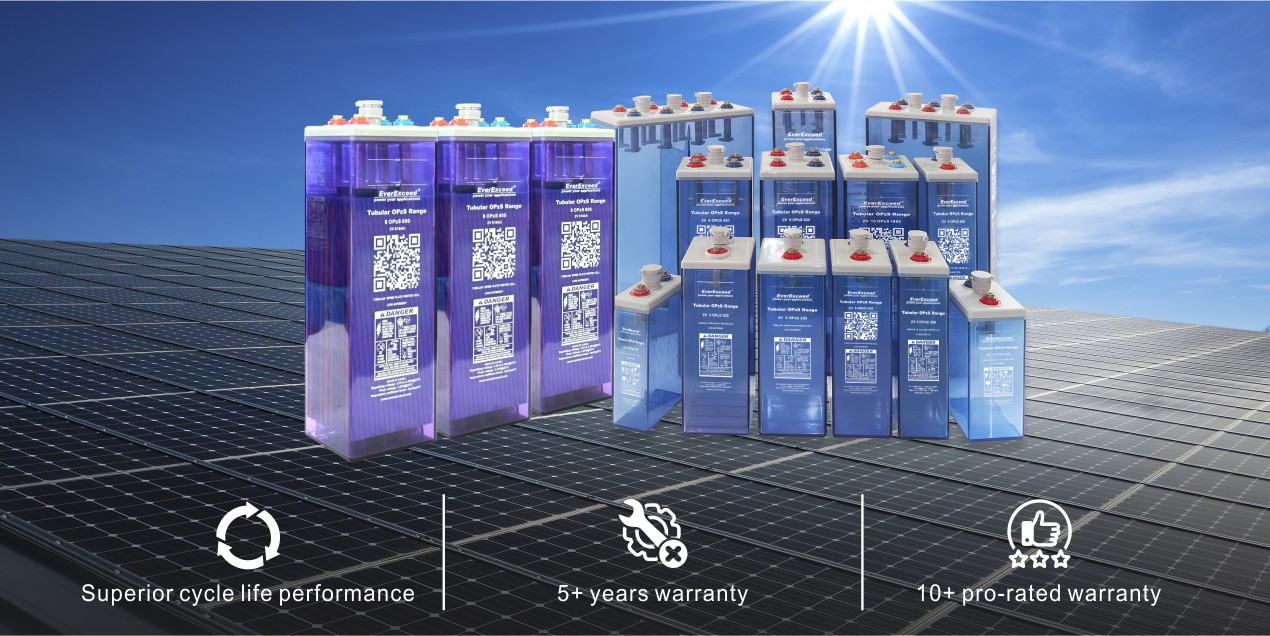
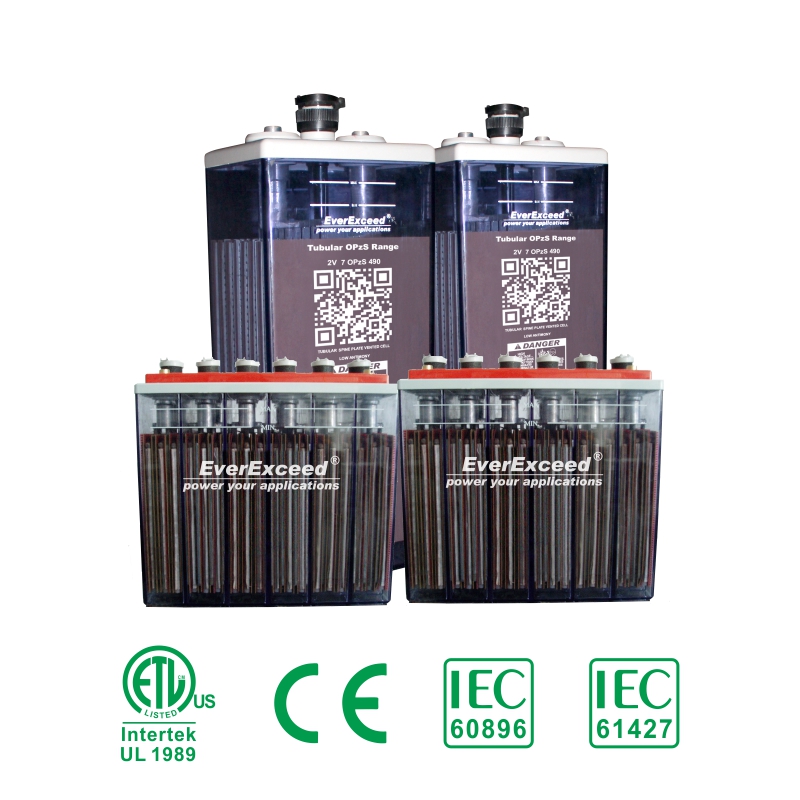
Flooded Battery (OPzS) is mainly used in telecommunication, base station, power plant, substation, backup and recycle power supply. Its advantages are long service life, good battery consistency, small voltage difference between float and charge voltage.
3. Flooded Lead Acid Battery use characteristics?
For Flooded Lead Acid Battery, after normal use for a period of time, due to the decline of the monomer electrolyte level, it is necessary to replenish its distilled water. The reasons for replenishing distilled water are as follows:
A. the battery in the late charging of 24 hours will produce the chemical reaction of electrolysis of water, the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen dissipated, so you can see the battery will bubble inside (the role of the electrolyte to stir the electrolyte, so that the electrolyte specific gravity of the electrolyte uniformity), which results in the loss of water in the electrolyte, the level of the liquid is lowered:
B. due to the battery itself in the use and charging process electrolyte temperature will rise (normal temperature rise of about 10 degrees), as well as the ambient temperature and other factors, the water in the electrolyte will continue to evaporate, resulting in electrolyte water loss, the liquid level is reduced. When the ambient temperature is high, it will accelerate the water evaporation, and the water loss of water evaporation is much larger than the water loss of electrolyte electrolysis.
C.Therefore, combined with the above two reasons m see, the battery high temperature, high ambient temperature, as well as charging, discharging current is too large and other factors will accelerate the liquid level drop (water loss). Therefore, rehydration is an important part of the maintenance process of liquid-rich lead-acid batteries. The battery can not be replenished under normal use.
4. What are the precautions for replenishment of liquid-rich lead-acid batteries?
A. water replenishment: after a period of time, the battery will be used for charging electrolytic water, temperature evaporation and other reasons lead to electrolyte reduction, the need for timely replenishment. Usually check the battery level once a week, if it is summer or higher temperature places, about three days should check the battery level. To the battery replenishment of water must use distilled water or deionized water.
B. to the battery water replenishment of common tools are: plastic measuring cups, simple water bucket, water car. In addition, you can also use the disposable water replenishment system. To the battery water cut off the use of metal utensils (except lead utensils)
C.in order to prevent the battery overfill and battery water shortage, the principle of water is added diligently, less added. Pay attention to the correct electrolyte level position when rehydrating the battery.
D.to prevent over-hydration:
That is, the water replenishment exceeds the prescribed level. Over-hydration or directly lead to electrolyte overflow, or during charging or operation lead to electrolyte overflow. The hazards are:
(1) lead to battery leakage, self-discharge:
(2) corrosion of battery poles, connecting strips, boxes, etc.:
(3) lead to a decline in battery capacity, resulting in the state of the monomer imbalance:
E, when the water replenishment is not timely resulting in a lack of water in the battery will cause:
(1) with the electrolyte surface will lead to a high temperature rise in the battery charging:
(2) the battery's capacity to decline:
(3) such as the plate is exposed to the air will cause its oxidation:
(4) the specific gravity of the electrolyte is elevated, easy to lead to corrosion deterioration of the plate: