The apparent power, active power, and reactive power meet the following triangular relationships:
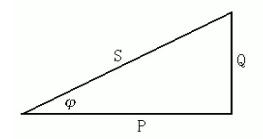
Figure (1): Schematic diagram of the power triangle
S:Apparent power S 2 =P 2 + Q 2
Q:Reactive power P = S *cosφ
P:Active power P = S *cosφ
φ :Power factor angle
Apparent power
The apparent power is generally expressed by S, the unit is VA 、 KVA, the apparent power represents the amount of AC electrical equipment capacity, which is equal to the product of the RMS value of voltage and the RMS value of current, and it
is multiplied by the power factor (PF) to equal the active power.
Active power
Active power is generally expressed by P, the unit is watts, kilowatts, and active power represents the actual AC energy generated or consumed per unit time, which is the average power in the cycle. In a single-phase circuit, it is equal to the product of the RMS voltage, RMS current, and power factor
Active power: The instantaneous power of alternating current is not a constantvalue, and the average value of instantaneous power in a cycle is called active power, therefore, active power is also called average power
Reactive power
The units of reactive power are Var and KVar. In a single-phase AC circuit, reactive power is equal to the product of the rms voltage, the rms current, and the sine of the phase angle between the voltage and the current.
Reactive power: The electrical power required to establish the alternating magnetic field and induced magnetic flux is called reactive power, therefore, the so-called "reactive" is not "useless" electrical power, but it is not converted into mechanical energy and thermal energy. Therefore, in addition to the active power supply, the reactive power supply is also needed in the power supply system, and both are indispensable.

