Anti reverse diode is usually used in power supply circuits to protect terminal devices from damage caused by reverse voltage and current. Without this anti reverse diode, reverse current may damage other components in the circuit. It is also common in battery powered mobile devices to protect the battery from damage from external devices.
Of course, anti reverse diode can not only prevent damage to other components caused by reverse current, but also prevent damage to the power supply or battery caused by reverse current. During the charging process of the battery, if the voltage exceeds the rated value or the charger is connected in reverse, it will cause the battery to charge in reverse and damage the battery. Under the protection of anti reverse diode, current cannot flow into the battery, avoiding this situation.
There are usually two types of anti reverse diodes: ordinary diodes and Schottky diodes. The characteristic of ordinary diodes is that the conduction current is small, while Schottky diodes have higher conduction current and lower reverse leakage current. In practical applications, appropriate anti backconnect diodes are selected according to the needs of the circuit.
Anti reverse diode is a very basic component that is widely used in various electronic devices, such as mobile phones, computers, battery chargers, etc. Its function is very important, as it not only protects other components from damage, but also protects the power supply or battery from damage.
1. Series anti reverse connection
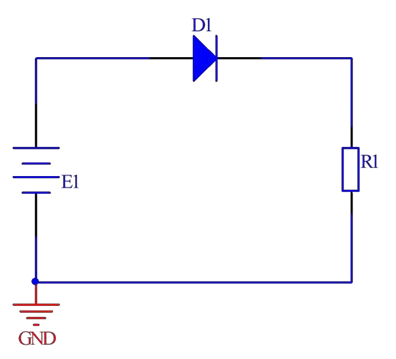
When E1 is directly connected, D1 is conducting, and the conduction voltage drop of D1 is VF. Therefore, the voltage applied to the load is E1-VF. The disadvantage of this circuit is that it will have losses, with a loss power of P=IL * VF. If there are requirements for the output voltage, the magnitude of D1's conduction voltage drop needs to be considered, so it is generally used in high-voltage situations. A high current circuit needs to consider the output current value of D1.
When the power supply E1 is connected in reverse, the reverse cut-off characteristic of the diode hinders the current flow and cannot form a circuit with the load R1, protecting the load. It should be noted that the maximum reverse peak voltage of the diode should be greater than the reverse voltage E1.
2. Joint prevention and reverse connection
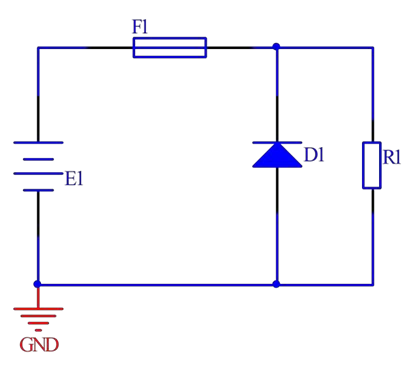
When E1 is directly connected, D1 is in reverse cutoff and the circuit is working normally;
When E1 is connected reversely, D1 is connected in the forward direction, and the reverse Voltage clamp is clamped at VF (diode conduction voltage drop), which needs to be less than the maximum reverse voltage of the load; On the other hand, when the fuse detects excessive circuit current, it will open to protect the back-end load. The disadvantage of this circuit is that it has an additional fuse, which increases the BOM cost. The selection of a fuse can restore the fuse.
This circuit can only prevent reverse connections, but if the input voltage is too high, it can still cause damage to the circuit. Therefore, D1 can be replaced with a voltage regulator diode to obtain good protection. The voltage regulation value of the voltage regulator diode should be selected to be less than or equal to the maximum normal working voltage of the subsequent circuit.
The principle of this circuit is that when the power supply E1 is reversed, the voltage regulator diode D1 conducts in the forward direction, and the negative pressure of the load is the conduction voltage VF of the diode, as described above. When the power supply E1 is directly connected and the input voltage is relatively high (such as greater than the voltage stabilizing value of the voltage stabilizing tube), due to the presence of the voltage stabilizing tube D1, the load terminal obtains a power supply of approximately the voltage stabilizing value VZ of the diode. So there will be a relatively high voltage (E1-VZ) on F1, and the current will rise quickly until F1 melts and the circuit is protected. This achieves overvoltage protection.
For parallel anti reverse connection circuits, the fusing current of the fuse should be greater than the normal working current of the subsequent load, and the circuit cannot be blown during normal use.
In addition, there are other applications of anti reverse diode.
a. To prevent reverse current from causing damage to sensors or interfaces, especially when external devices are connected to the system, anti reverse diodes can protect sensors and interfaces from damage from external devices.
b. To prevent damage to high-precision circuits caused by reverse currents, anti reverse diodes can protect high-precision circuits from interference from reverse currents.
c. Prevent reverse current from causing damage to relays or other mechanical components. Relays and mechanical components are sensitive components, and anti reverse diodes can protect them from reverse current damage.
In short, anti reverse diode is an important protective element in the circuit. Its function is very important to prevent reverse current from damaging other components. Designers need to consider the use of anti reverse diodes in circuit design to protect the normal operation of the circuit.
scan to wechat:everexceed
